Eye is like a camera. Camera has a lens in the front and a film or sensor at the back. Retina is like the film or sensor of the camera. It is found in the back part of the eye and it is the screen on which the image is formed.
Retina Diseases are managed by an eye surgeon who specializes in management of Retina Diseases. Dr. Gaurav Shah who has studied about Retinal diseases from Sankara Nethralaya, Chennai, L V Prasad Eye Institute, Hyderabad and University of Florida, USA is the Director of Retina Services at Eye Life.
OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography)
– It is a laser-based scanning machine which can scan the retina, cornea and optic nerve to evaluate retinal diseases, corneal diseases and glaucoma. Eye Life uses a high definition imported OCT machine to give safe, non-invasive analysis of the retinal disease and glaucoma within minutes.
Retina Laser
It is a form of light treatment given to the retina. The treatment is usually given in the sitting position in the OPD (Out Patient Department, Consulting Room). Types of retina laser include
1. Macula laser to reduce edema / swelling in the macula part of the retina.
2. Retina laser done to prevent bleeding in the eye in Diabetic Retinopathy, BRVO (branch retinal vein occlusion), CRVO (central retinal vein occlusion), and other retinopathies.
3. Barrage retina laser done to strengthen the retina and reduce risk of Retina Detachment.
Intravitreal injection
Under anaesthesia, painless injection allows medicine to quickly reach the retina and provide quick treatment. Eye Life provides various types of Intravitreal Injections such as Avastin (Bevacizumab), Zaltrap, Accentrix (Ranibizumab – Lucentis), Pagenax (Brolucizumab), Eylea (Aflibercept), Vabysmo (Faricimab), Triamcinolone and Ozurdex. Our retina team will guide you to their advantages and disadvantages, specifically based on your eye condition.
Microscope for Retina Surgery
Unlike operating microscope for cataract and other eye surgeries which focus on the front part of the eye, retina surgeries require high end microscope with a capability to view the back part of the eye. Eye Life uses an advanced German Zeiss microscope with BIOM to allow clear visualization of retina and perform safe retina surgery.
Vitrectomy Machine
This is an advanced machine which allows robotic retina surgery with the help of delicate instruments which enter the eye to remove diseased or abnormal tissues and replace them with various types of fluid or gas. Eye Life uses a high-speed sutureless system which allows safe and stitchless retina surgery.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy is a retinal disease that occurs as a result of uncontrolled and long-standing diabetes. Commonest complication of people suffering from diabetes include decreased vision which can be due to diabetic cataract or retinal diseases called as Diabetic Retinopathy in which there is swelling of the retina or bleeding in front of the retina. It can manifest as mild blurring of vision in the early stages and progress to sudden vision loss and blackouts caused by bleeding in the eye in advanced cases. Diabetic retinopathy is managed by control of diabetes along with intravitreal injection, retinal laser or retina surgery based on the severity of the disease as assessed on OCT scan. If detected in time, permanent blindness can be prevented and hence it is advised that every diabetic should get retina evaluation done at least once a year or sooner if risk of vision threatening diabetic retinopathy is high as assessed by the retina specialist.
BRVO (branch retinal vein occlusion)
In BRVO, one of the main veins of the retina gets blocked. This leads to bleeding in the retina and swelling of the macula of the retina and results in decrease in vision. It is usually caused due to increased blood pressure with / without diabetes. It can be confirmed by OCT scan and effectively managed by intravitreal injections, laser and surgery.
CRVO (central retinal vein occlusion)
When all the veins of the retina get blocked, it is called as CRVO. Loss of vision occurs due to bleeding in the whole of the retina and severe swelling of the retina. It occurs due to increased blood pressure with / without diabetes. It is commonly treated by intravitreal injections and sometimes requires laser and surgery.
Retinal Detachment and Lattice Degeneration
When the retina gets torn from its base, it is called as Retinal Detachment. Retinal detachment can result in sudden vision loss, with patients describing a curtain-like black out in their visual field. Retinal detachment is considered an emergency and requires surgical treatment by a qualified retina specialist. Retina Detachment occurs due to ageing. People with nearsightedness (minus number glasses) are more prone to developing retinal detachment. Usually, floaters (grey / black particles seen against light coloured background) and flashes of light in front of the eye precede Retinal Detachment. Hence, any person having floaters or flashes of light and every person with minus spectacle number should be examined by a Retina Specialist every year. If during retina examination, Lattice Degeneration or weakening of the retina is detected, barrage retina laser can be done to strengthen the retina and reduce the risk of retinal detachment. Floaters, if obstructing vision, can be surgically removed.
ERM (Epi Retinal Membrane)
Due to ageing or eye disease, a membrane forms over the retina and causes wrinkling of the screen of the eye (retina). This leads to damage to the retina and decrease or distortion in vision. If operated before irreversible damage occurs to the retina, surgery can help in improvement of distortion as well as quality of vision.
Macular Hole
Macular Hole is a hole in the centre of the retina which is the most important part of the retina. Wherever a person with macular hole looks, she / he will see blurred, distorted or hazy image. Advancements in retina surgery allows repair of macular hole and good chance of visual recovery.
AMD (Age related Macular Degeneration)
AMD refers to damage to the central part of the retina due to age-related factors. It typically affects both eyes, and patients may experience a black spot in their central vision. AMD is of two types – Dry and Wet. Dry AMD is more common but less vision threatening. It is managed by medicines. Wet AMD is also called as MNV (Macular Neo Vascularisation) and is vision threatening. Diagnosis is usually confirmed through an OCT scan and it also helps to differentiate between the dry and wet type of AMD. Injection of a medicine directly near the retina helps prevent further loss of vision and also improve vision if done early in the timeline of the disease.
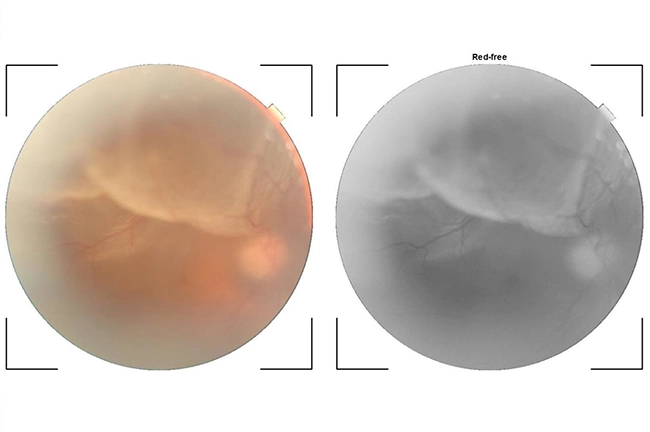
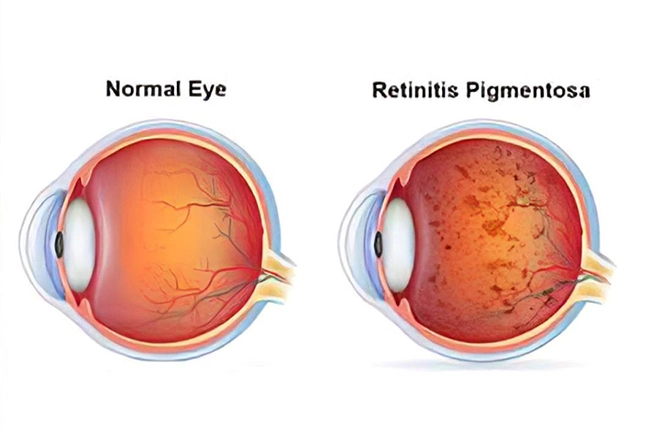
Retinitis Pigmentosa and Retinal Degenerations or Dystrophies
Retinitis Pigmentosa and Retinal Degenerations or Dystrophies are hereditary retinal conditions associated with decreased vision. Retinal investigations such as OCT can give an idea about the vision and many times they require low vision aids to improve vision.
Hypertensive Retinopathy
Hypertensive retinopathy occurs due to damage to the blood vessels supplying the retina. It can progress slowly and, in some cases, cause sudden vision loss due to hemorrhage. Regular eye check-ups with a retina specialist can aid in early diagnosis of this condition, while strict monitoring of blood pressure is also essential.
Vitreous Haemorrhage
Bleeding inside the eye is called as vitreous haemorrhage. It can occur due to Diabetic Retinopathy, BRVO, CRVO, AMD, Retina Detachment / Tears. If bleeding is minimal, person will see floaters or grey to black clouds. If bleeding is extensive, it obstructs light from reaching the retina and person loses complete vision. In such cases, it is important to find out the cause of bleeding. Often, Intravitreal Injections are used to temporarily stop continuous blood accumulation in front of the retina. If the bleeding is massive or the blood clot does not get absorbed, retinal surgery / vitrectomy helps in clearing the blood and improving vision. After removing the blood, retinal laser can be done during the surgery to reduce risk of recurrence of bleeding.
CSCR (Central Serous Chorio-retinopathy)
– In CSCR accumulation of fluid beneath the retina causes blurred vision. It is diagnosed on OCT scan and is treated with macula laser.
Myopic Fundus
People with high myopia develop thin retina which can lead to lattice degeneration and risk of retinal detachment. Hence, their retina needs to be checked every year.
Floaters
Floaters are often seen as grey (various shades between white and black) particles, resembling dots, insects, wavy lines or a circle in one’s field of view. They often cause limitation in everyday living, reading and work due to their floating around unexpectedly wherever one tries to look. In case of large floaters, vision can get decreased. Floaters may occur due to ageing process in the vitreous jelly in front of the retina of the eye, bleeding within the eye or retinal problems such as retinal hole or retinal detachment. Hence, it is imperative that in case of sudden appearance of Floaters, retina evaluation after dilation of pupil of the eye should be by a Retina Specialist. Treatment can involve medical management, lasers and if floaters are large or chronic and interfering with lifestyle or work than floaterectomy surgery, which is usually a suture-less (stitch-less) surgery, can be done to remove the floaters. Please contact Retina Services at Eye Life for complete evaluation of the problem so that they can guide you with the appropriate management.