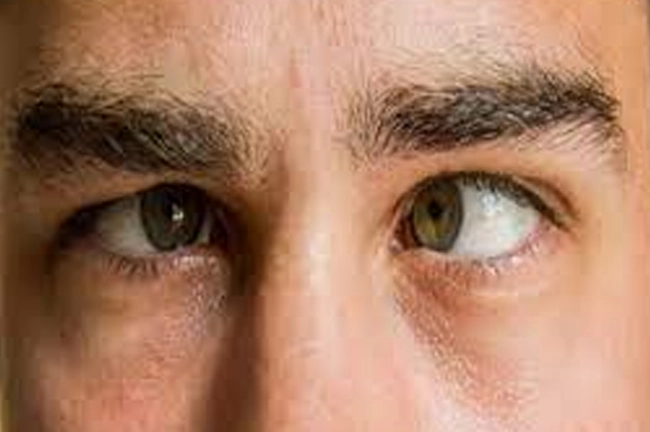
Squint, also known as strabismus, refers to a condition in which the two eyes do not align or move in the same direction. It is commonly observed in children but can also occur in adults. Diagnosing squint in children is important as it may be associated with decreased vision in one eye. If left untreated in children, squint can lead to a condition called lazy eye (amblyopia), resulting in permanent vision loss. Treatment for squint in children often involves the use of glasses, and in some cases, surgery may be required. In adults, squint can develop as a result of an injury or accident. Individuals with diabetes may also experience the sudden onset of squint due to nerve problems. Squint treatment in adults usually involves surgery.